Implement Serverless Architecture with Azion
Serverless computing allows you to build and run applications without worrying about the underlying infrastructure. With Azion Edge Platform, you can focus more on creating quality products and less on managing servers.
The benefits of serverless are numerous: it offers scalability, cost-efficiency, and speed. By leveraging Azion Edge Functions, you can implement your business logic closer to the end user, resulting in ultra-fast, responsive applications. Dive into this guide to explore the architecture and implementation of serverless applications on Azion.
Architecture
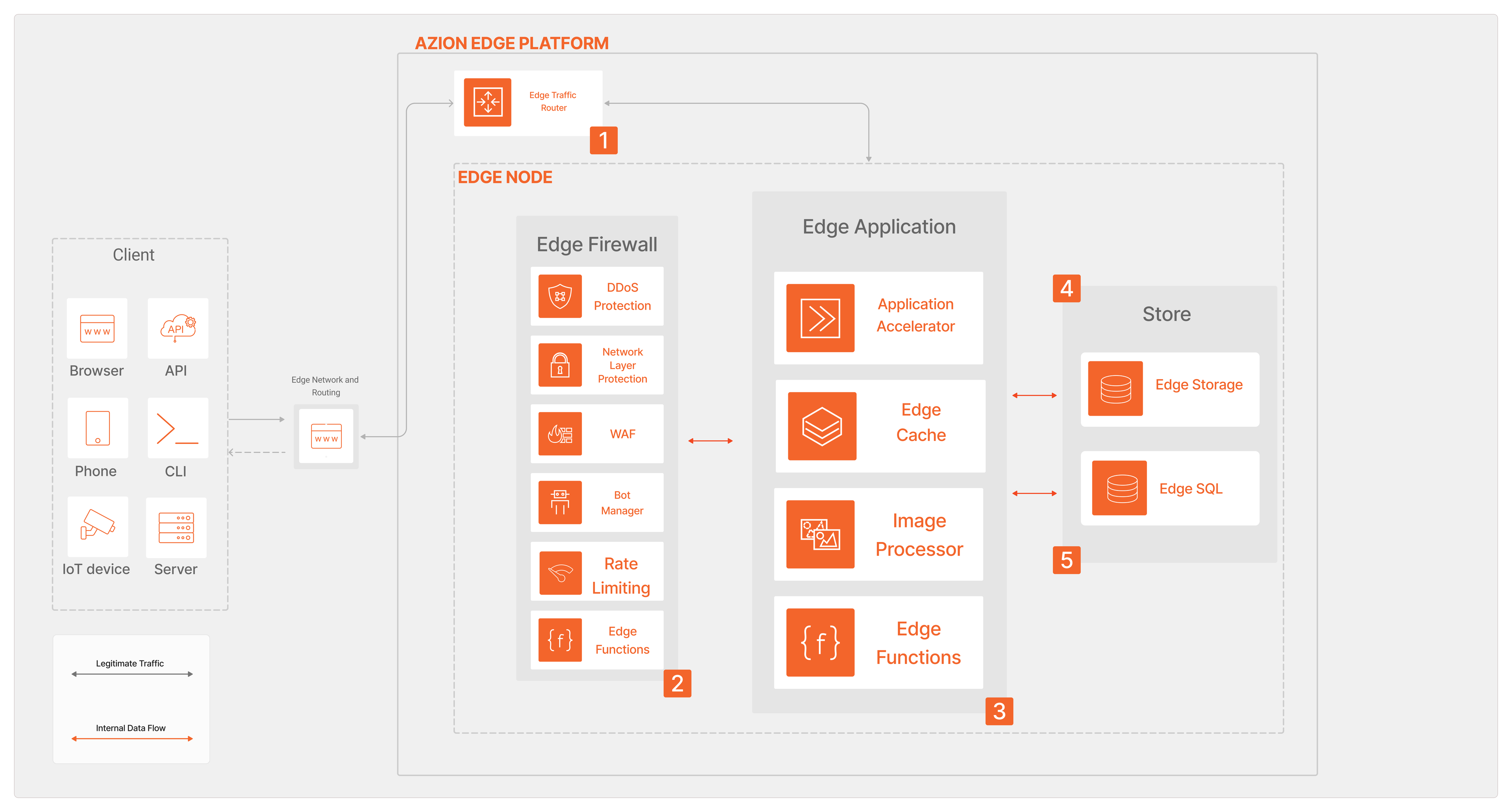
Dataflow
-
The user accesses the Domain related to the Edge Application being accessed. This request goes to Azion Traffic Router, which chooses the optimal Edge Node to receive the request and directs the request to this Edge Node.
-
The request goes through Edge Firewall and is analyzed. If it’s not a malicious request, it goes forward and reaches the Edge Application.
-
The request reaches the Edge Application and based on its Rules Engine configuration, accesses the requested content. If configured, Image Processor, Edge Cache, Application Acceleration, and Edge Functions will be executed.
-
The content, if static, will be stored in Edge Storage. So, it’ll be requested and returned as a response.
-
Operations requiring database transactions can be accomplished with Edge SQL.
After all this process, the content is delivered to the client.
Components
- Edge Application: allows you to set up an edge application to configure delivery and cache policies, create rules to automate cache policy assignments based on content type, and determine how content is cached.
- Edge Cache: global module to cache content at the edge.
- Edge Functions: allows you to create event-driven, serverless applications, at the edge of the network, closer to users.
- Rules Engine: a tool to configure the scenarios in which a specific cache policy is enforced.
- Tiered Cache: module that creates an additional cache layer between the edge and your origin servers, reducing latency and infrastructure costs.
- Load Balancer: module designed to balance traffic across your origins, data centers, or cloud providers, mitigating network congestion and server overload.
- Edge Storage: a scalable and secure storage service designed to integrate object storage with the Azion Edge Platform using the S3 standard for object operations.
- Origins: allows you to customize the source address of your Edge Application content, the Host header of your application, the path, and the HMAC authentication credentials for protected services.
- Domains: register a custom domain with Azion to deliver the edge application.
Implementation
- Create an edge application:
- Create a domain and associate it with the edge application:
- On Console, create a domain using the + Create button on the homepage.
- Use the Azion API to create a domain. If you created an application through a template, the domain is created for you.
The edge application is accessible through the domain provided by Azion, which looks similar to:
ftd1cvntfl.map.azionedge.net
- Test and monitor: after configuring your content delivery, thoroughly test the content delivery to ensure it’s functioning as expected and monitor incoming access.
- Make adjustments to caching policies, rules, or other configurations as needed based on performance metrics and user feedback.
Related docs
Contributors