Implement Microservices Applications with Azion Edge Functions
Adopting a serverless microservices architecture with Azion Edge Functions brings several significant benefits in this context. Firstly, it improves scalability by allowing each service to scale independently based on its own demand, rather than scaling the entire application based on the demand of a single service. This leads to more efficient resource utilization and cost savings.
Additionally, it enhances flexibility by allowing each service to be developed, deployed, and updated independently. This means that changes can be made to one service without impacting the others, enabling faster innovation and reducing the risk of system-wide failures.
Architecture
Dataflow
-
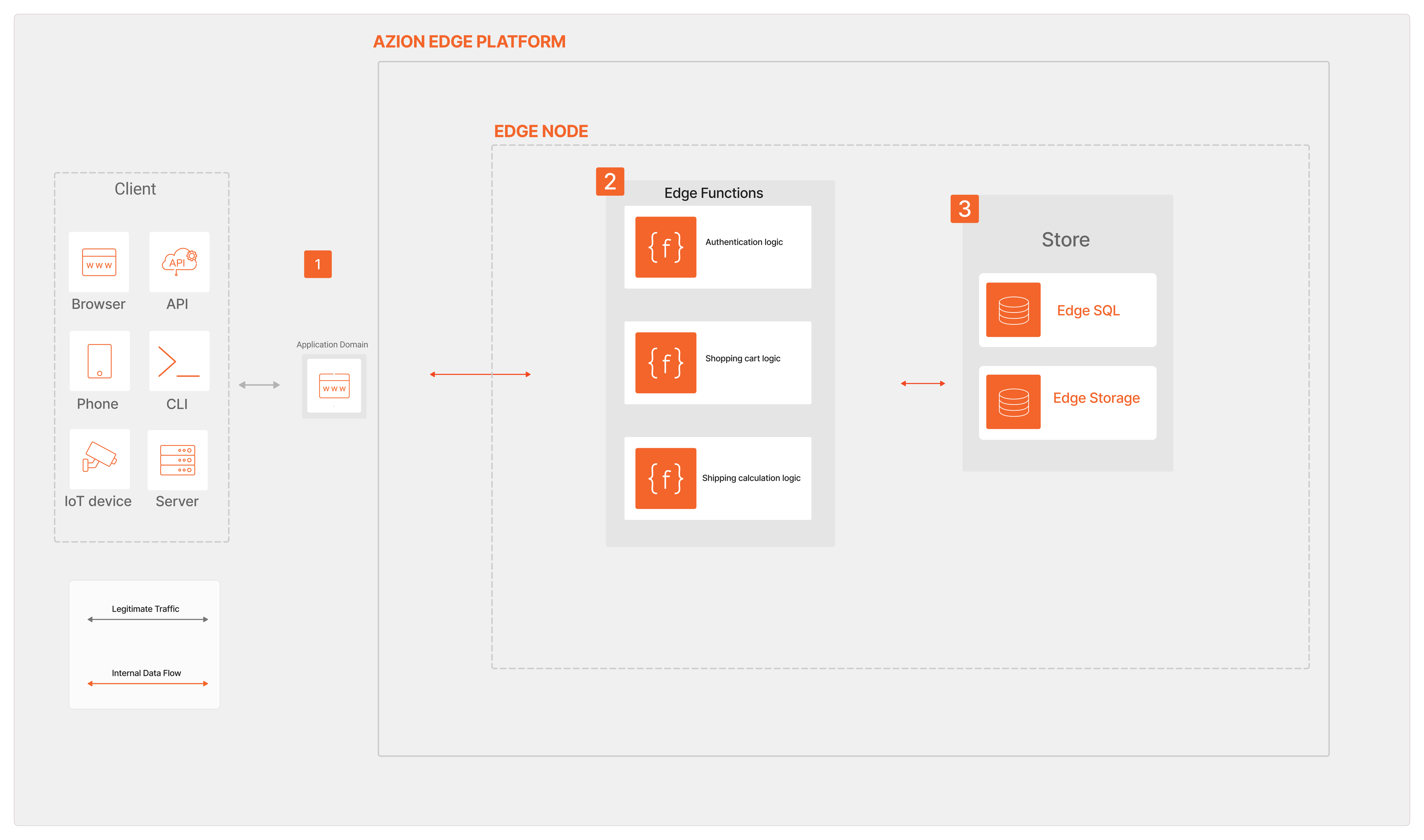
A user sends a request to the Domain associated with an edge application. This request is directed to the Azion Traffic Router, which identifies the appropriate Edge Node to process the request.
-
At this stage, based on microservice architecture, the request branches out to different services in response to the Rules Engine configuration. This branching out means the services can evolve independently, facilitating faster innovation cycles and quick deployment of new features.
-
Edge Functions are invoked. Each service in a microservices architecture corresponds to different business capabilities. For example, an Authentication Middleware service handles user authentication, a Shopping Cart service manages user cart operations, and a Shipping Calculation service computes shipping costs. These services are developed in Javascript, deployed, and scaled independently, providing agility and resilience.
-
Static content gets saved in Edge Storage from where it’s fetched and served as a response. This leverages edge computing to ensure lower latency and faster content delivery.
-
Edge SQL handles operations involving database transactions. This further emphasizes the separation of concerns, with every service taking ownership of its specific database to ensure loose coupling and high cohesion.
After these distinct yet cohesive processes, the content —processed and assembled— is delivered back to the client. This microservices-oriented data flow with edge computing ensures highly efficient, scalable, and resilient operations, offering considerable business advantages.
Components
- Edge Application: set up an edge application to configure delivery and cache policies, create rules to automate cache policy assignments based on content type, and determine how content is cached.
- Edge Functions: allows you to create event-driven, serverless applications, at the edge of the network, closer to users.
- Edge Storage: a scalable and secure storage service designed to integrate object storage with the Azion Edge Platform using the S3 standard for object operations.
- Edge SQL: an edge-native SQL solution designed for serverless applications. It’s fully ACID-compliant and utilizes SQLite’s SQL dialect to provide a familiar development environment, facilitating fast integration.
Implementation
- Create an edge application:
- Create an edge function and instantiate it in the recently created application.
- Create a domain and associate it with the edge application:
- On Console, create a domain using the + Create button on the homepage.
- Using the Azion API to create a domain.
- If you created an application through a template, the domain is created for you.
- Test and monitor your edge application.
Related docs
Contributors