Optimize and process images with Azion Edge Platform
Azion Image Processor offers simplicity and automation to resource management, allowing you to cut back on load times and storage costs. Running on a distributed edge computing network, you can reduce image sizes, crop and resize images to fit your needs, and apply filters to the image. All using one single image file.
Architecture
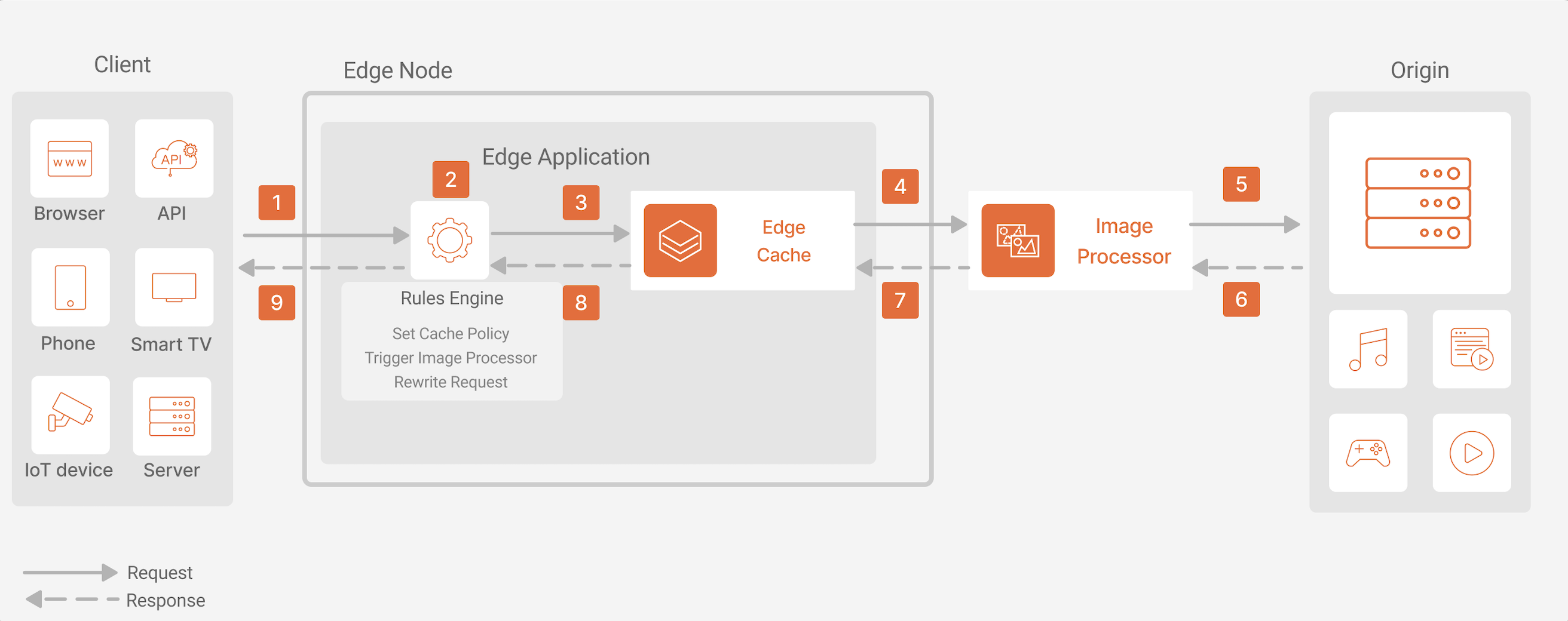
Dataflow
- A user makes a request to a domain associated with an edge application.
- In the edge node, the request is processed by Rules Engine. The cache policies and image optimization behavior are enabled in the request phase.
- If configured, image optimization algorithms and Runtime functions are executed.
- The request passes through the Edge Cache layer. If a cache key exists for the object, a match is found and the object is delivered.
- If a cache key doesn’t exist for the object, the request is forwarded to the origin.
- The origin responds with the content to the edge node.
- The object is cached in the Edge Cache layer, and a cache key for the object is generated and added to the
X-Cache-KeyHTTP header in the response. - The object returns to the application layer. For upstream objects (from the origin), any policies and directives that should be applied to the object are processed by Rules Engine and enforced.
- Content is delivered to the user.
Components
- Edge Application: set up an edge application to configure delivery and cache policies, create rules to automate cache policy assignments based on content type, and determine how content is cached.
- Edge Cache: global module to cache content at the edge.
- Rules Engine: a tool to configure the scenarios in which a specific cache policy is enforced and activate image optimization.
- Image Processor: an add-on that allows image manipulation through the request line.
- Domains: register a custom domain with Azion to deliver the edge application.
Implementation
-
Create an edge application: you must first create the content delivery application layer at the edge of the network. You can do that using Azion Console, Azion API or Azion CLI.
- Choose the Image Optimization template to accelerate the process. To easily deploy this template at the edge, click the button below:
-
Create a domain and associate it with the edge application:
- On Console, create a domain using the + Create button on the top navbar.
- Use the Azion API to create a domain.
- If you created an application through a template or the Azion CLI, the domain is created for you.
-
Set up cache policies: configure a cache policy for images. The recommended setup is:
- Images: define cache settings for image files to optimize delivery. For images, it’s recommended to keep them cached at the edge for longer periods, such as 1 year (31536000 seconds).
-
Enforce cache policies in specific scenarios: use Rules Engine to enforce specific policies based on various conditions. Create and modify the rules:
- Default rule: activate Image Processor with the behavior Optimize Images.
- Images: for image files, apply the appropriate cache policy.
-
Apply image processing algorithms to your application:
- Apply
?imsqueries from the code of the application itself. - Create a rule to rewrite the request URL to add the
?imsquery.
- Apply
-
Point the domain to Azion: update your DNS settings to point your domain’s CNAME record to the Azion endpoint provided for your domain.
-
Test and monitor: after configuring your content delivery, test the content delivery to ensure it’s functioning as expected and monitor incoming access.
-
Make adjustments to caching policies, rules, image optimization, or other configurations as needed based on performance metrics and user feedback.