Boost Content Delivery Speed and Reliability at the Edge
Edge-native content delivery architectures empower developers to replace legacy CDNs and leverage the speed and reliability of the edge network while reducing costs. Azion Edge Platform minimizes latency and enables dynamic content and advanced features, processing requests at the edge closest to end-users. This comprehensive approach allows developers to build and deploy high-performance, scalable applications that enhance user experience and improve Core Web Vitals scores, surpassing the limitations of traditional CDN solutions.
This solution is ideal for organizations looking to modernize their content delivery strategy, reduce infrastructure costs, and deliver exceptional digital experiences to their users.
Content Delivery Architecture Diagram
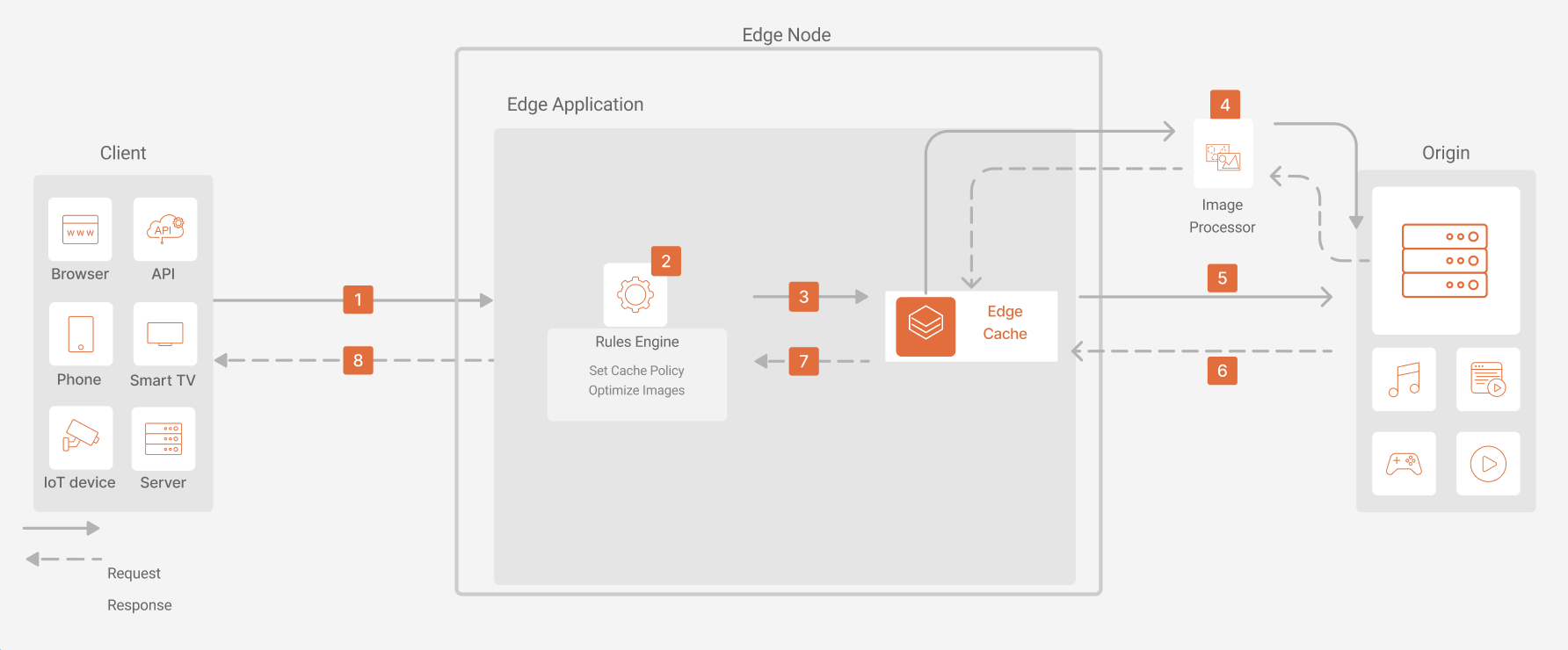
Content Delivery Dataflow
- A client sends an HTTP or HTTPS request to a domain associated with an edge application.
- At the edge node, the Rules Engine processes the request, enabling cache policies and image optimization behavior during the request phase.
- The request is then evaluated by the edge cache layer. If a cache key exists for the requested object, a match is found, and the object is delivered from the cache.
- If configured, Image Optimization retrieves the image from Origin and executes image processing algorithms. Edge Node cache the optimized image.
- If a cache key doesn’t exist for the object, the request is forwarded to the origin server.
- The origin server responds with the content, which is then cached at the edge node. A cache key for the object is generated and included in the X-Cache-Key HTTP header of the response.
- Before the object is returned to the client, any additional policies and directives applicable to the object are processed and enforced by the Rules Engine.
- Finally, the content is delivered to the user.
Components
- Edge Application: set up an edge application to configure delivery and cache policies, create rules to automate cache policy assignments based on content type, and determine how content is cached.
- Edge Cache: global add-on to cache content at the edge.
- Application Accelerator: used to customize cache optimization rules and cache keys and cookies based on established patterns.
- Rules Engine: a tool to configure the scenarios in which a specific cache policy is enforced.
- Image Processor: that allows image manipulation through the request line.
Implementation
- Create an edge application: you must first create the content delivery application layer at the edge of the network.
- On Console, create an application using the + Create button on the homepage.
- Use the Azion API to create an edge application.
- Use the Azion CLI to create and deploy an edge application.
- Choose the Dynamic and Static File Optimization template.
- Create a domain and associate it with the edge application:
- On Console, create a domain using the + Create button on the homepage.
- Use the Azion API to create a domain.
- If you created an application through a template, the domain is created for you.
- Set up cache policies: configure cache policies for different types of content. The recommended setup is:
- Static files: configure cache policies for static assets. The recommended setup is to cache at the edge for at most 15 days (432000 seconds).
- Images: define cache settings for image files to optimize delivery. For images, it’s recommended to keep them cached at the edge for longer periods, such as 1 year (31536000 seconds).
- Enforce cache policies in specific scenarios: use Rules Engine to enforce specific policies based on various conditions. Create two rules:
- Static files: for static files such as music, video, or executables, apply the appropriate cache policy.
- Images: for image files, apply the appropriate cache policy.
- Point domain to Azion: update your DNS settings to point your domain’s CNAME record to the Azion endpoint provided for your domain.
- Test and monitor: after configuring your content delivery, thoroughly test the content delivery to ensure it’s functioning as expected and monitor incoming access.
- Make adjustments to caching policies, rules, or other configurations as needed based on performance metrics and user feedback.
Related docs
Contributors